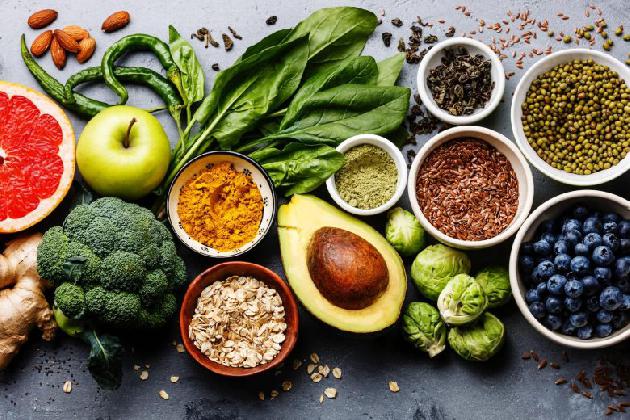
We all know more or less the concept of vegetarian diet: It could be defined as a diet that enhances the consumption of vegetable foods and abstains or decreases products of animal origin.
This type of food has a clear upward trend … But is it really a healthy eating option?
Well the answer is yes, as long as we do them in a balanced way. According to the American Dietetic Association (ADA) and other public health institutions well-planned vegetarian diets are appropriate for all stages of the life cycle, and are a nutritionally healthy choice, but if they are performed incorrectly they can cause health problems.
When you stop eating certain foods, there are some nutrients that we have to pay more attention to: Let’s get to know some of the main ones!
Nutrient
Calcium
If dairy products (cheese or milk) are not included in the vegetarian diet, we would have to increase the consumption of green leafy vegetables (broccoli, spinach, white beans, kale …) to obtain this nutrient. In addition, there are options for vegetable drinks enriched in calcium.
Iron
The iron that comes from vegetable foods (iron not emo) has less assimilation. But there is a trick to improve this absorption: Eat it in the same meal with foods rich in vitamin C (tomato, pepper, citrus) and avoid the intake of calcium-rich foods (yogurt or milk sauces)
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 in a vegan diet can only be contributed either by the intake of supplements or by fortified foods such as, for example: cereals, vegetable drinks, nutritional yeast, etc. Foods such as seaweed, fermented soy, or tofu have been credited as sources of vitamin B12, but studies show that it has no true vitamin activity.
Vitamin D
This vitamin is very important since it regulates the passage of calcium to bone. In a vegetarian diet your main intake is in enriched drinks, but the best way to avoid deficiency of this vitamin is through a 30-minute daily exposure to the sun.
Finally, remember that, in this type of diets, what we discussed in the previous post is important: We can obtain protein of high biological value (equivalent to animal protein) from a correct combination of vegetable protein.